Rare ‘meat-eating’ plants, missing from North West England for more than 100 years, are making a comeback in Manchester.
The endangered and little known great sundew (Drosera anglica) - a carnivorous plant which was once commonly found in England - has suffered a dramatic decline over the last century, becoming extinct in most regions.
Changes in land use across the country for agriculture has led to the drying of the moist wetlands the plants need to survive.
Since the turn of the 19th century, drainage, eutrophication and peat extraction have nearly driven the great sundew out of England entirely.
But now, the rare and unusual plant has been given a much-needed boost by a team of conservationists working to prevent the extinction of Britain’s carnivorous flora. In a partnership between the Lancashire Wildlife Trust, Chester Zoo, and pioneering young conservationist, Joshua Styles, The Manchester Mosslands Species Reintroduction project is carrying out the crucial safeguarding and reproduction of rare carnivorous plant species, and reintroducing them to key sites around the North West.
Ten individual plants, successfully cultivated by Mr Styles, have been planted on the conservation site so far. It is hoped they will now thrive and reproduce in the protected area. Mr Styles, from the North West Rare Plant Initiative (NWRPI), has been instrumental in the orchestration of the reintroduction.
He said: “If we were to do nothing, it is extremely likely that this carnivorous plant would become extinct in England in the very near future, and we’re not prepared to sit back and watch that happen.
“The work that NWRPI, Chester Zoo and Lancashire Wildlife Trust are doing will, hopefully, guarantee the presence of this amazing, rare and endemic carnivorous plant in England for years to come.
“The leaves of this striking plant are coated in many tiny tentacles, tipped with droplets of what at first appears to be morning dew – giving the plant its name. These droplets though are actually globules of a really sticky, sweet-smelling liquid which is simply irresistible to passing insects.
“Any curious insect unfortunate enough to become entrapped has no chance of escape. The sundew’s tentacles roll up and tighten around its prey, smothering and drowning the insect in the sticky fluid. Digestive enzymes are then slowly secreted, breaking the insect down into a meal which it then absorbs. Eventually, the leaf unfurls, freeing the little that’s left behind - an empty insect exoskeleton.”

 Match Report - Macclesfield Town 0 - 1 Brentford
Match Report - Macclesfield Town 0 - 1 Brentford
 Update on Flag Lane Baths
Update on Flag Lane Baths
 Council supports stronger measures to curb smartphone use in Cheshire schools
Council supports stronger measures to curb smartphone use in Cheshire schools
 Man arrested following M6 police pursuit
Man arrested following M6 police pursuit
 Appeal following collision in Macclesfield
Appeal following collision in Macclesfield
 Call for sites launched to help shape new Cheshire East Local Plan
Call for sites launched to help shape new Cheshire East Local Plan
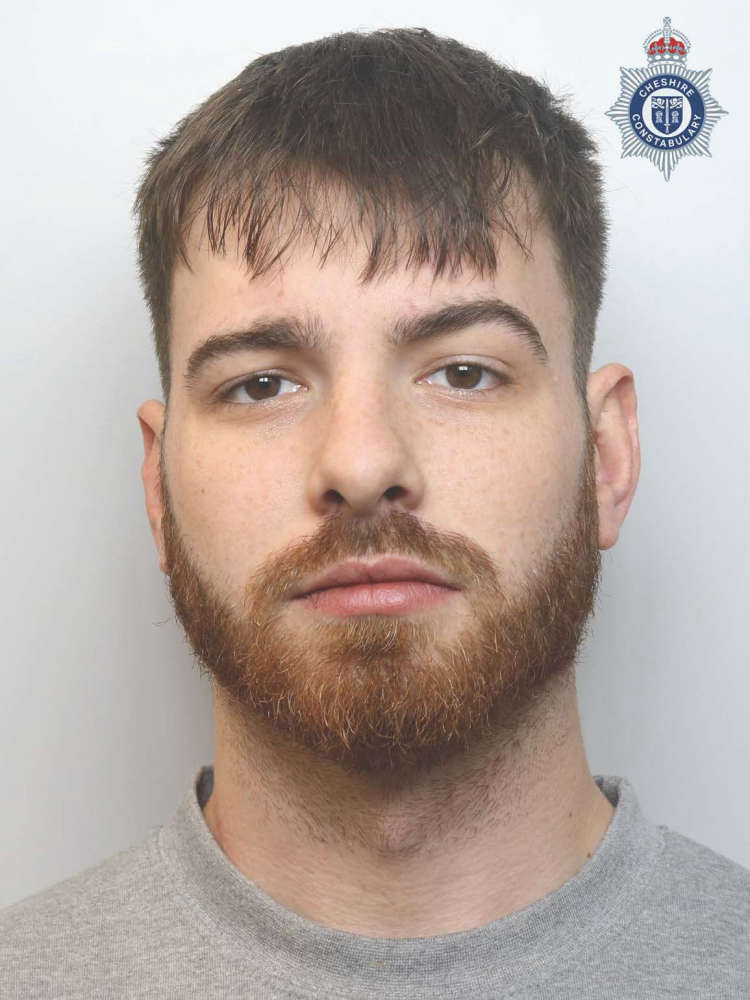 Man jailed for selling cannabis after previously being spared prison
Man jailed for selling cannabis after previously being spared prison
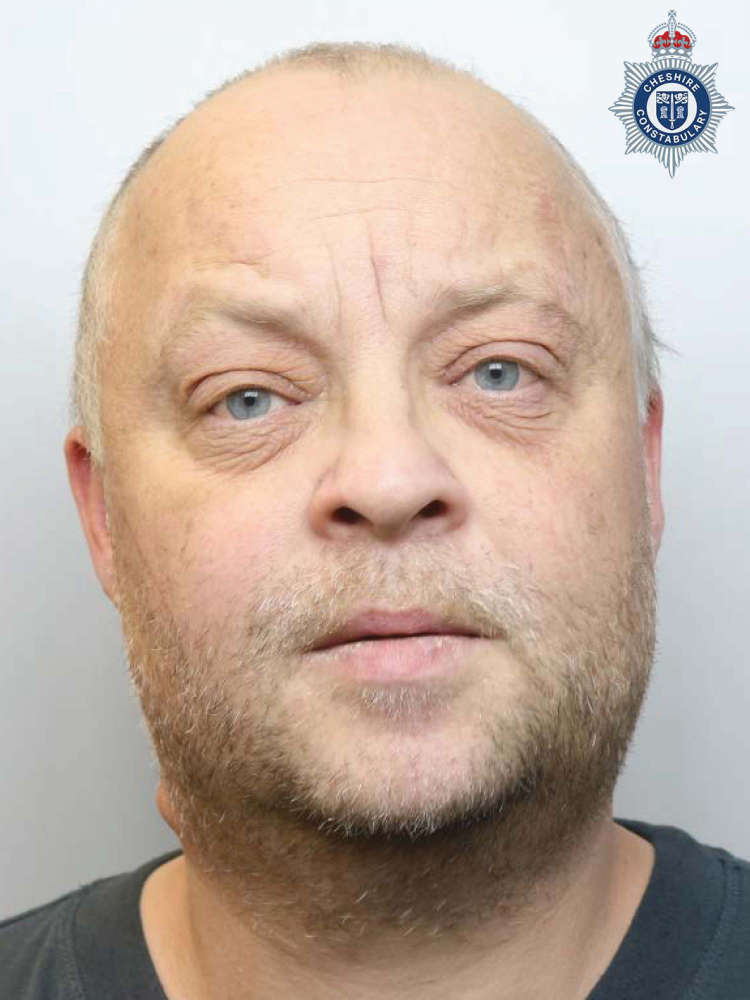 Predator jailed for 26 years in Northwich
Predator jailed for 26 years in Northwich
 Applications for council’s warmer homes scheme are open
Applications for council’s warmer homes scheme are open
 Man charged with making nuisance calls to police
Man charged with making nuisance calls to police
 Man jailed for seven years for drugs offences in Crewe
Man jailed for seven years for drugs offences in Crewe
 MACCLESFIELD’S SILK MUSEUM UNVEILS VIBRANT PROGRAMME FOR WOMEN’S HISTORY MONTH
MACCLESFIELD’S SILK MUSEUM UNVEILS VIBRANT PROGRAMME FOR WOMEN’S HISTORY MONTH
 Vital investment for fire and rescue service agreed by councillors
Vital investment for fire and rescue service agreed by councillors
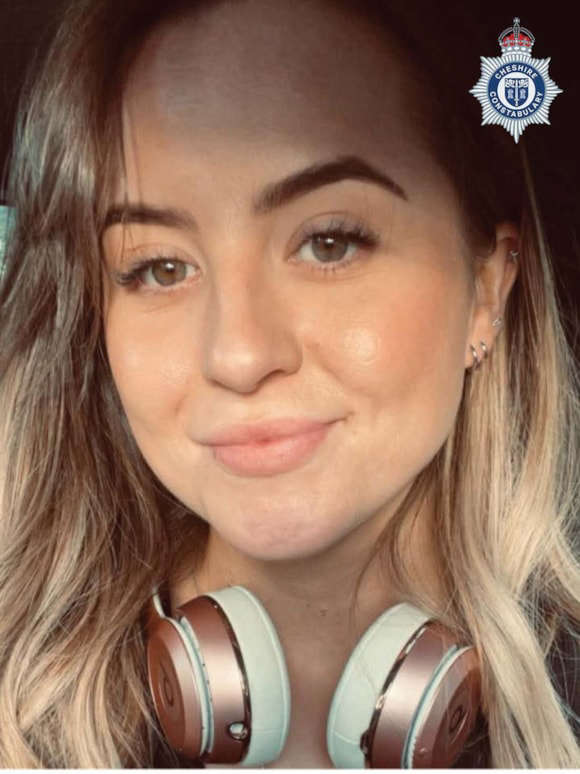 Tributes issued to off-duty officer following fatal collision in Arclid
Tributes issued to off-duty officer following fatal collision in Arclid
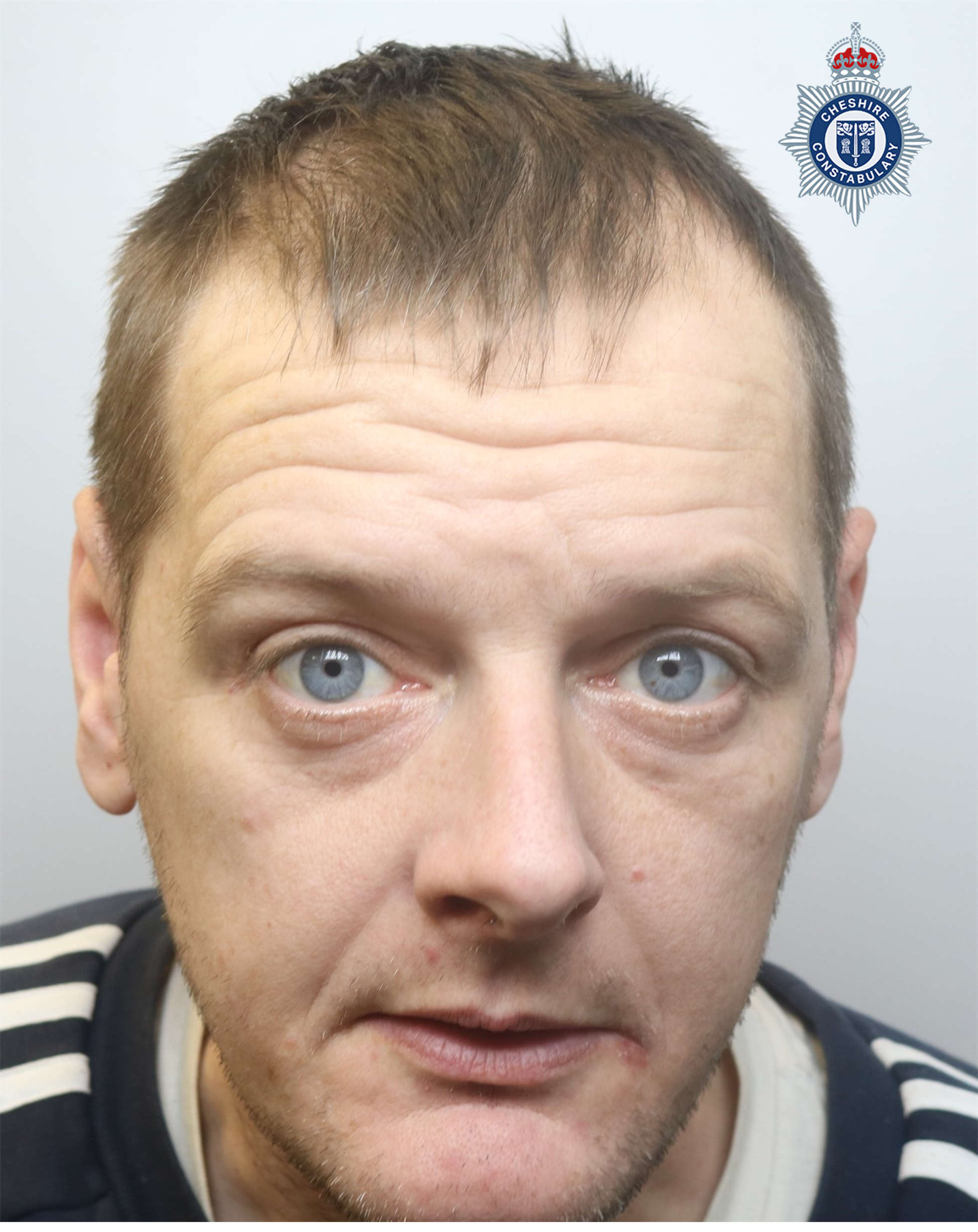 Criminal Behaviour Order bans prolific shoplifter from every Co-Op in Macclesfield and nine other retailers
Criminal Behaviour Order bans prolific shoplifter from every Co-Op in Macclesfield and nine other retailers
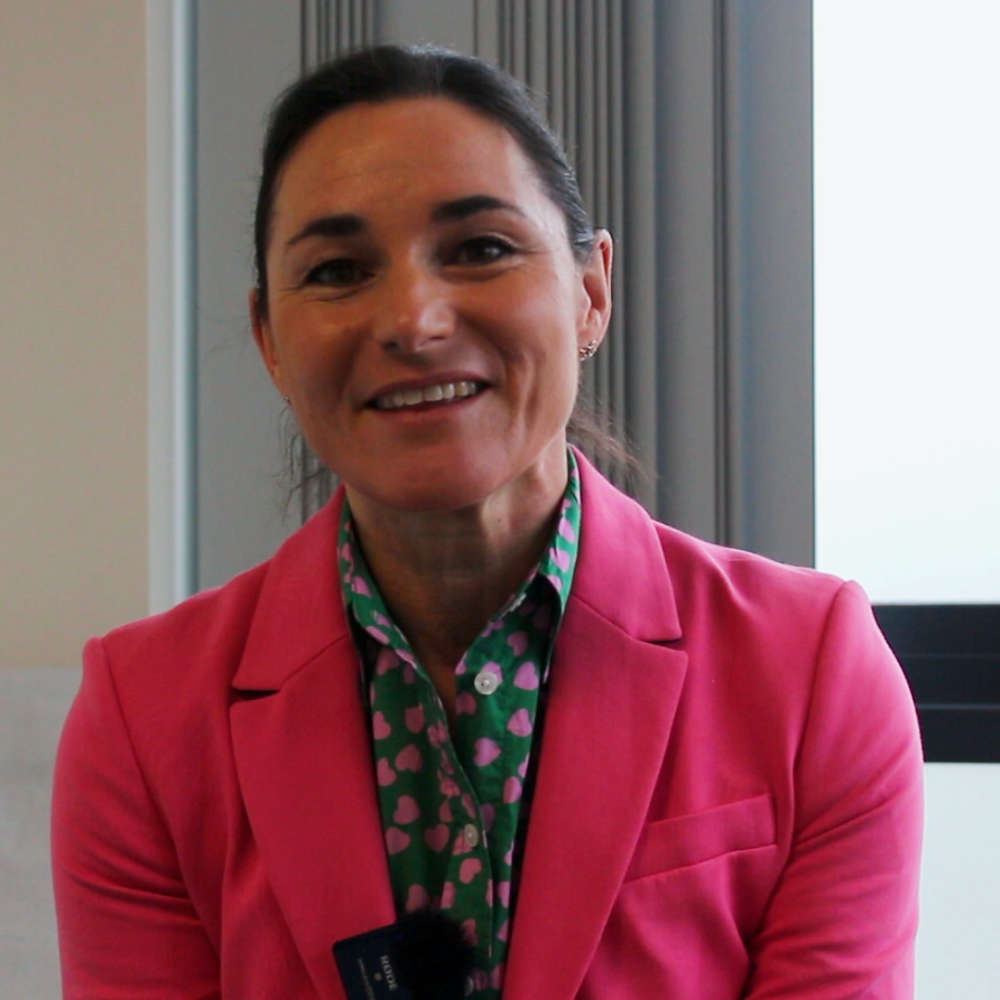 Dame Sarah Storey champions early breast cancer detection at Macclesfield Hospital
Dame Sarah Storey champions early breast cancer detection at Macclesfield Hospital
 Appeal for information following fatal collision in Arclid
Appeal for information following fatal collision in Arclid
 £19k worth of illicit tobacco and cigarettes seized from retailers as part of force-wide day of action
£19k worth of illicit tobacco and cigarettes seized from retailers as part of force-wide day of action